Hansoh Pharma's CD19 mAb Xinyue opens a new era of reimbursable drugs for rare disease NMOSD
We are committed to being the opinion leader platform for the pharmaceutical industry. We record and observe major business events in the pharmaceutical industry, showcase the complexities and conflicts in this industry, and provide insight into cutting-edge industry trends.
In recent years, the National Healthcare Security Administration has been supporting the inclusion of rare disease drugs into the National Reimbursable Drug List by continuously optimizing the adjustment procedure of the list. In 2022, the National Reimbursable Drug List has even opened a separate application channel for rare disease drugs to support their priority inclusion. Therefore, after the release of the latest medical insurance negotiation results, whether innovative drugs for rare diseases are included has become the focus of attention.
On January 18,2023, the National Healthcare Security Administration and the Ministry of Human Resources and Social Security announced the medical insurance negotiation results in 2022. Hansoh Pharma's highly anticipated drug for the rare disease NMOSD (neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders), Xinyue (inebilizumab injection), became the first and only reimbursable drug for NMOSD in China after successful negotiation.
China is the country with the largest number of NMOSD patients, but patients here have long been faced with the dilemma of not having access to drugs and not being able to afford drugs. The inclusion of Hansoh Pharma's Xinyue in the National Reimbursable Drug List this time will undoubtedly significantly improve the accessibility and affordability of medication for NMOSD patients in China, making sequential and long-term treatment possible.
New medical insurance trend: "Chinese Speed" accelerates global access to breakthrough innovative drugs
It must be admitted that, in the five years after the establishment of the National Healthcare Security Administration, the drug price negotiations have been improved in terms of procedures and rules each year. As the dynamic adjustment of the National Reimbursable Drug List becomes regular, on the one hand, the average time from the approval of an innovative drug for marketing to its inclusion in the National Reimbursable Drug List has been shortened to about 1.1 years; on the other hand, more high-value innovative drugs and rare disease drugs have been included in the National Reimbursable Drug List, benefiting a wider range of patients.
"Every small group should not be abandoned." In the history of rare diseases in China, 2018 is an important watershed. In this year, five ministries and commissions jointly issued the Notice on Publishing the Catalogue of the First Batch of Rare Diseases. Since then, this document, as "China's first official definition of rare diseases", has sounded the "rallying cry" for rare disease diagnosis and treatment, and with the further implementation of the national policy, more and more rare disease drugs have been included in the National Reimbursable Drug List. Nusinersen sodium, a drug for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) that entered the National Reimbursable Drug List in 2021, is the best example, which brings hope to both rare disease patients and rare disease drug developers. In 2022, the National Reimbursable Drug List has been further adjusted. In particular, the time limit for rare disease drugs has been lifted, and a separate application channel has been opened to support their priority inclusion in the National Reimbursable Drug List.
Driven by the policy, pharmaceutical companies have also shown a positive attitude. In 2022, the number of rare disease drugs involved in national negotiations has increased to 19, including drugs for SMA, Fabry disease, Gaucher disease, multiple sclerosis, NMOSD and other rare diseases. Most of these products come from multinational pharmaceutical companies and only a few are owned by local pharmaceutical companies.
According to a source close to the National Healthcare Security Administration, local pharmaceutical companies have been more active on the whole. For example, Hansoh Pharma's inebilizumab injection has been successfully included as a reimbursable drug in the first medical insurance negotiation after its approval for marketing. This is a major achievement of joint efforts between the National Healthcare Security Administration and local innovative pharmaceutical companies, and also demonstrates China's speed to address the urgent clinical needs of rare disease patients and to accelerate the accessibility and affordability of breakthrough innovative drugs worldwide.
Inebilizumab injection was first approved for marketing by the U.S. FDA in June 2020, and the marketing authorization application was based on a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (N-MOmentum) evalsuating the efficacy and safety of inebilizumab injection for the treatment of NMOSD - the largest RCT study for the treatment of NMOSD to date. The trial enrolled 231 adult patients, 213 of whom were anti-AQP4 antibody positive, and the 197-day study showed that the 161 anti-AQP4 antibody positive patients treated with inebilizumab had a 77% reduction in the risk of NMOSD recurrence, a significant reduction in disease progression, number of active MRI lesions and risk of hospitalization, and an adverse event rate comparable to placebo.
Inebilizumab was granted orphan drug status by the FDA and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) prior to approval and was granted breakthrough therapy designation (BTD) by the FDA due to its clear target, outstanding efficacy and significant differentiation.
In May 2019, Hansoh Pharma, which has been hunting for good drugs worldwide, noticed this drug and invested heavily to get the development and commercialization rights of inebilizumab injection in China from Viela Bio, Inc. for a total amount of up to USD 220 million. After the deal was concluded, Hansoh Pharma quickly implemented its plan to market inebilizumab injection in China and, with the strong support of the country's rare disease policy, received marketing approval from the National Medical Products Administration in March 2022, significantly shortening the global time lag for drug launch.
It is worth mentioning that inebilizumab injection was also approved for marketing by the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) in March 2021 and by the EMA in May 2022, and was listed as a Class A recommended drug in China's Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders (2021) in December 2021.
Effectively reduce patients' disease burden and help them improve their quality of life
NMOSD is a rare neurological autoimmune disease with high recurrence and high disability, mainly involving the optic nerve and spinal cord. China currently has the largest NMOSD patient base in the world, and the disease is highly prevalsent in the young and middle-aged female population. Patients are often disabled and impoverished by the disease, resulting in serious medical and social burdens.
Previous treatments for the acute phase of NMOSD in China include hormone, plasma exchange (PE), immunoadsorption (IA) and intravenous human immunoglobulin. According to some clinical medical professionals, any clinical attack of NMOSD may bring irreversible damage, and the accumulation of neurological dysfunction after each attack is the main cause of disability. Therefore, for patients with AQP4-IgG positive and AQP4-IgG negative relapse course, sequential therapy (relapse prevention therapy) should be started as soon as possible after diagnosis and long-term therapy should be persisted.
Despite the tough situation, the reality is that there used to few sequential therapy products for NMOSD in China before, basically in the state of very limited availability or accessibility. Reportedly, in China, only satralizumab and inebilizumab have been approved for corresponding indications, and after the adjustment of the National Reimbursable Drug List this time, inebilizumab has become the first and only NMOSD treatment drug to enter the National Reimbursable Drug List.
Inebilizumab is an innovative drug for the treatment of adult patients with anti-AQP4 antibody positive NMOSD and a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody targeting CD19 on the surface of B cells. It binds specifically to the B cell surface antigen CD19, leading to CD19 + B-cell depletion. Compared to CD20, CD19 is expressed in a broader range of B-cell lineages, from pre-B cells to plasma mother cells and certain plasma cells. Therefore, direct depletion of CD19 + B cells can more effectively reduce the risk of NMOSD relapse and disability progression by more efficiently depleting AQP4-IgG producing plasma cells in a safe and reliable manner, which is expected to meet the urgent need for therapeutic drugs for the overall benefit of NMOSD patients.
From this, we can see that the inclusion of inebilizumab into the National Reimbursable Drug List is of great significance to NMOSD patients in China, which will significantly improve the accessibility, affordability and standardization of clinical treatment for NMOSD patients in China, and effectively help patients to reduce relapse, minimize disability and return to normal life.
Building a benign ecosystem - experts call for improving the multi-level guarantee mechanism for rare disease drugs
For Hansoh Pharma, the inclusion of inebilizumab as its first approved innovative biologic drug into the National Reimbursable Drug List has positive implications for the commercialization and expansion of its biologic drugs. Inebilizumab is known to have extensive (up to 10) clinical development pipelines globally, with NMOSD being the fastest indication to enter the market. Hansoh Pharma has chosen to enter the National Reimbursable Drug List at this time to (i) increase the accessibility of the drug, (ii) leverage the product's first-mover advantage to quickly capture the market, and (iii) in the longer term, rely on the indications already in the National Reimbursable Drug List to quickly complete access preparation and guide subsequent approved indications. According to the data, the two indications of myasthenia gravis and IgG4-related diseases have been advanced to phase III clinical trials in China.
Global clinical development pipeline of inebilizumab: targeting a wide range of autoimmune diseases and hematologic tumors
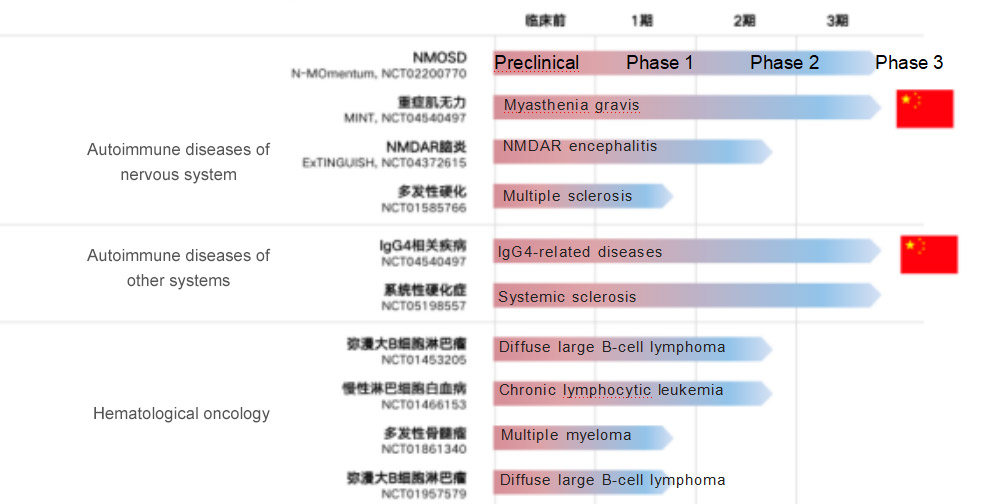
From the introduction and approval of Xinyue to the inclusion in the new National Reimbursable Drug List, the "Chinese Speed" behind will undoubtedly drive more local pharmaceutical companies like Hansoh Pharma to enter the field of innovative drugs for rare diseases and increase the enthusiasm for rare disease drug development.
Xinyue has made a good start, but there is still a long way to go to further solve the "last mile" problem after the inclusion of high-value innovative drugs for rare diseases in the National Reimbursable Drug List so as to effectively ensure the accessibility of drugs for rare disease patients.
In this regard, some experts suggest that the government, enterprises, and society should cooperate to consolidate and improve the multi-level guarantee mechanism to supplement the national basic medical insurance, mainly in the forms of special funds, medical insurance for serious diseases, medical aid, and commercial medical insurance.
We believe that only by building a multi-level guarantee system for rare disease drugs through multi-party efforts, can we truly achieve a win-win benign ecosystem that provides affordable rare disease drugs for patients, sustainable medical insurance funds and guarantee for enterprises.

